Surface Area Heat Transfer . an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. A is the area of heat transfer; by the end of this section, you will be able to: T s is the surface temperature; T f is the fluid temperature; Let us understand the importance. If you knock apart the. h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer;
from www.slideserve.com
A is the area of heat transfer; by the end of this section, you will be able to: an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. T s is the surface temperature; Let us understand the importance. finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer;
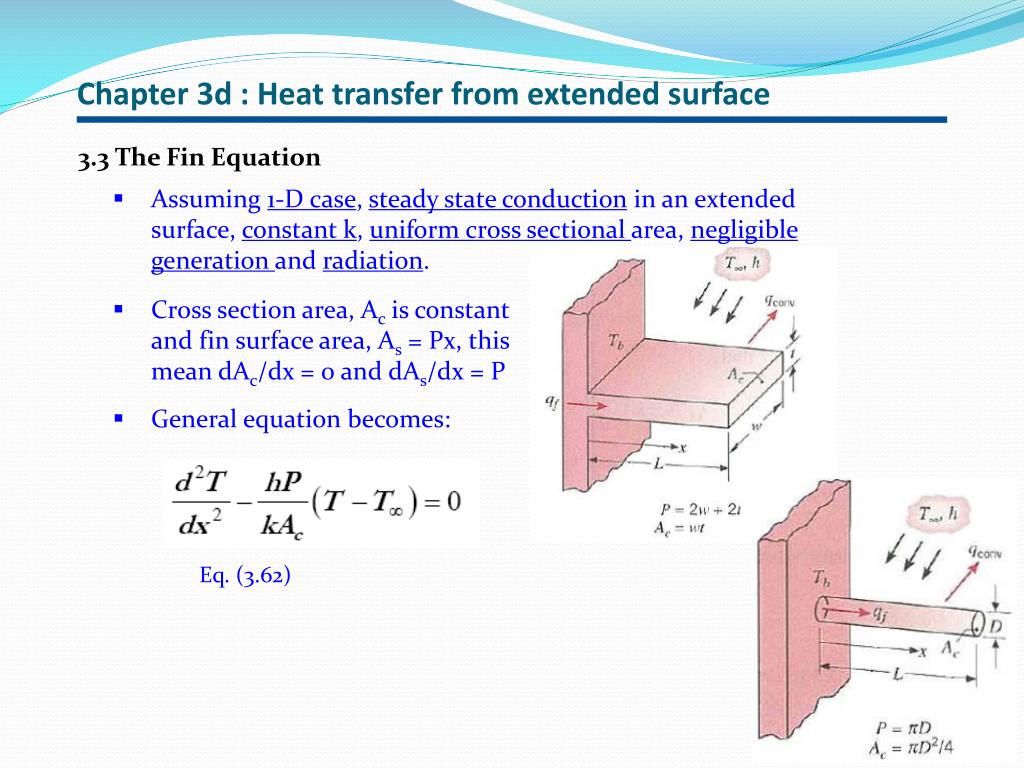
PPT 1D, Steady State Heat Transfer with Heat Generation Fins and
Surface Area Heat Transfer T s is the surface temperature; Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. If you knock apart the. an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. by the end of this section, you will be able to: T s is the surface temperature; As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer; T f is the fluid temperature; finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. Let us understand the importance. A is the area of heat transfer; surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer.
From www.nuclear-power.com
Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient Definition Surface Area Heat Transfer the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. surface area available for heat transfer is quite. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From news.mit.edu
Understanding how fluids heat or cool surfaces MIT News Surface Area Heat Transfer the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. Let us understand the importance. finally, the radiated heat. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 4 Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces PowerPoint Surface Area Heat Transfer As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. If you knock apart the. T s is the surface temperature; finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. A is the area of heat transfer; by the end of. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.youtube.com
Heat Transfer Thermofluids Determine steady rate of heat transfer Surface Area Heat Transfer the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer; T f is the fluid temperature; surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.researchgate.net
43 Heat transfer surface area density β, m 2 /m 3 Download Scientific Surface Area Heat Transfer Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. If you knock apart the. h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer; A is the area of heat transfer; As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT HEAT EXCHANGERS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4204670 Surface Area Heat Transfer If you knock apart the. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. T f is the fluid temperature; A is the area of heat transfer; an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. surface area available for heat transfer is quite. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Problem 5 Heat transfer by convection and radiation [20 pts Surface Area Heat Transfer T s is the surface temperature; surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. T f is the fluid temperature; finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From studylib.net
Extended Surface Heat Transfer Surface Area Heat Transfer the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. T f is the fluid temperature; If you knock apart the. surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideshare.net
Thermodynamics Chapter 3 Heat Transfer Surface Area Heat Transfer T s is the surface temperature; the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. T f is the fluid temperature; A is the area of heat transfer;. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heat Transfer Coefficient PowerPoint Presentation, free download Surface Area Heat Transfer an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. If you knock apart the. Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. T s is the surface temperature; h c is the coefficient of convective heat transfer; surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.studyiq.com
Heat Transfer Types, Definition, Convection, Radiation, Conduction Surface Area Heat Transfer T s is the surface temperature; If you knock apart the. surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. by the end of this section, you will be able to: As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat.. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Conduction Physics Surface Area Heat Transfer by the end of this section, you will be able to: surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. T s is the surface temperature; As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. If you knock apart the.. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From 2ch204ns2013.wordpress.com
Extended Surface Heat Transfer Theory part 2 CH302 Heat Transfer Surface Area Heat Transfer an object with a wider area has more surface particles working to conduct heat. the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. If you knock apart the. finally, the radiated heat is proportional to. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 1D, Steady State Heat Transfer with Heat Generation Fins and Surface Area Heat Transfer the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of the pipe and the length (l) of the pipe. T f is the fluid temperature; surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. h c. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.youtube.com
Heat Transfer Determine the rate of heat transfer between the plates Surface Area Heat Transfer T f is the fluid temperature; Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. by the end of this section, you. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.youtube.com
Heat Transfer L22 p3 Bulk Temperature Constant Heat Flux YouTube Surface Area Heat Transfer finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. Let us understand the importance. Explain some phenomena that involve conductive, convective, and radiative. As such, the rate of heat transfer is. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 1D, Steady State Heat Transfer with Heat Generation Fins and Surface Area Heat Transfer finally, the radiated heat is proportional to the object’s surface area, since every part of the surface radiates. by the end of this section, you will be able to: As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. T f is the fluid temperature; surface area available for. Surface Area Heat Transfer.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED P5.16 Convection heat transfer data are often reported as a Surface Area Heat Transfer surface area available for heat transfer is quite an important determinant of the overall rate of heat transfer. As such, the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area through which the heat. the surface area (a) for transferring heat through the pipe (neglecting the pipe ends) is directly proportional to the radius (r) of. Surface Area Heat Transfer.